Human Normal Microbiota Begin to Develop
This is the normal microbial population. They participate in quantifiable physiological processes and have evolved together with our species thanks to the fact that they have.
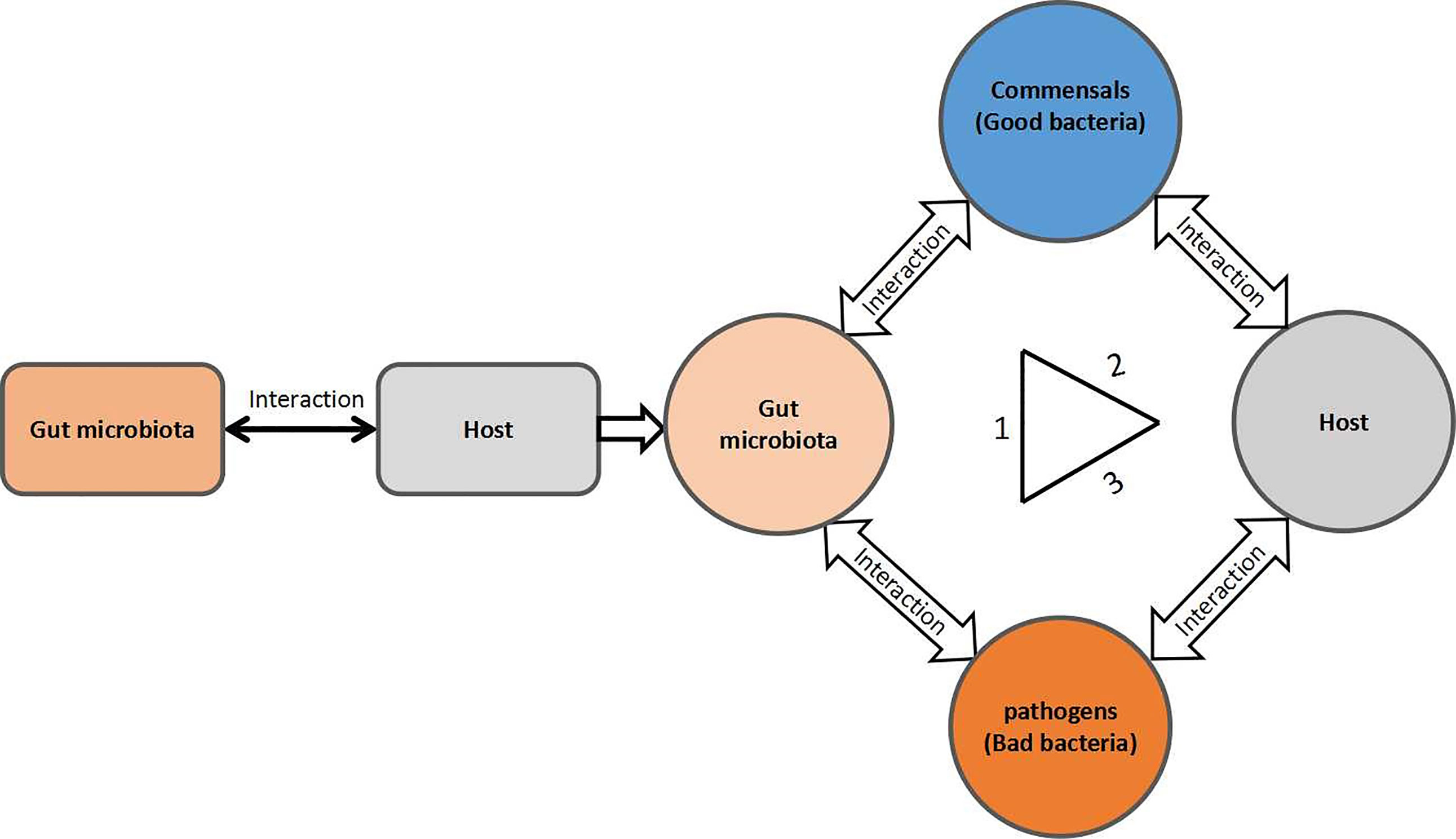
Frontiers Mechanism Of The Gut Microbiota Colonization Resistance And Enteric Pathogen Infection Cellular And Infection Microbiology
DrTVRao MD NORMAL HUMAN FLORA DRTVRAO MD 1 2.

. Human normal microbiota first begin to develop _. 1965 Gut microbiota transfer experiments in germ-free animals MILESTONE 3 1972 The microbiota influences metabolism of host-directed drugs MILESTONE 4 1981 Microbiota succession in early life MILESTONE 5 1996 Sequence-based identification of human associated microbiota MILESTONE 6 1998 Stability and individuality of adult microbiota. The normal flora in humans usually develops in an orderly sequence or succession after birth leading to the stable populations of bacteria that make up the normal adult flora.
The human microbiome refers to the spectrum of microbes microbiota that colonize humans. Papers began emerging in 2013 showing that the normal biliary microbiota is a separate functional layer which protects a biliary tract from colonization by exogenous microorganisms. The average human body contains 1013 cells and harbors 1014 bacteria.
HUMAN MICROBIOME DRTVRAO MD 2 The human microbiome or human micro biota is the aggregate of microorganisms that reside on the surface and in deep layers of skin in the saliva and oral mucosa in the conjunctiva and in the gastrointestinal tracts. These studies have shown a great variability. 2225 It was once believed that the gut microbiome had approximately 10 times more microbial cells in the human gut than the entire human body.
Less common are Peptococcus Streptviridens Enterococcus Micrococcus Eschcoli Candida. A growing body of evidence indicates that the. The human microbiome is largely made commensal orgood bacteria and microbes which lives mainly in our gut and is thought to out number human cells 101.
Immediately after birth there seems to be a decrease in gut alpha diversity48 49 probably reflecting the selective pressure of the substrate constraints of milk and by 1 week of age the gut microbiota is already very similar to that in a month-old baby50 Infants develop during the first 6 months under the selective pressure of milk shaping the gut microbial communities whose. On the other hand the most common oral diseases caries gingivitis and. The normal microbial fauna is stable.
The oral microbiota represents an important part of the human microbiota and includes several hundred to several thousand diverse species. Development of the human GI microbiota The development of the microbiota is generally believed to begin from birth although this dogma is challenged by a limited number of studies in which microbes were detected in womb tissues such as the placenta 23 24. The set of all these populations give rise to the normal microbiota which we divide into two categories.
More specifically it refers to the microbial genomes of all the bacteria fungi protozoa and viruses. Host-microbiome interactions have been associated with a variety of disease states and more recent data is beginning to elucidate mechanistic insight into how host-microbiota interactions promote specific diseases. Normal Human Flora 1.
Learn More About How Microbiome Restoration May Reduce C. A literature search was done using PubMed Cochrane and EMBASE databases. Chapter 14- Infection Infectious Disease and Epidemiology 1.
The human microbiome or microbiota is defined as the collection of microbes - bacteria viruses and single-cell eukaryotes - that inhabits the human body. It is a normal part of the oral cavity and has an important function to protect against colonization of extrinsic bacteria which could affect systemic health. These are the microorganisms that live in our body for an indefinite or prolonged time.
Human bodies rely on the innumerable bacterial genes as the source of essential nutrients. Microbes in a healthy human adult are estimated to outnumber human cells by a ratio of ten to one and the total number of genes in the microbiome may exceed the number of genes in the human genome by a factor of about 100. MODULE Normal Flora of Human Body Microbiology 82 Notes Microorganisms present on the skin surface are Staphepidermidis and Diphtheroids are the most common.
From shortly after birth to death the skin and mucous membranes are home to a diverse microbial fauna. View Test Prep - Chapter 14 from BIO 2342 at El Centro College. In particular the gastrointestinal microbiome gut microbiome or GM has received significant attention in recent years due to its distinct connections to metabolic endocrine immunological and neurological activity and function.
This paper reviews the published evidence on early-life intestinal microbiota development as well as the different factors influencing its development before at and after birth. The bacterial component of the human microbiota is the subject of most studies including a large-scale project started in 2008 called Human Microbiome Project whose aim is to characterize the microbiome associated with multiple body sites such as the skin mouth nose vagina and intestine in 242 healthy adults. Collectively these microbiota form an ecosystem thought to consist of.
Human normal microbiota begin to develop. Herein we review normal microbiome development as well as common mechanisms of dysbiosis in the context of pathophysiology. Diff Treatments May Offset the Gut Microbiome Resulting in Recurrent Infection.
View Test Prep - TEST QUESTIONS MED MICRO from BIO 2400 at Texas State University. These microbiota are symbiotic and we depend on them for our health and well being as much as they do on us. The main factor determining the composition of the normal flora in a body region is the nature of the local environment which is determined by pH temperature redox potential and oxygen water and.
Test questions med micro final.
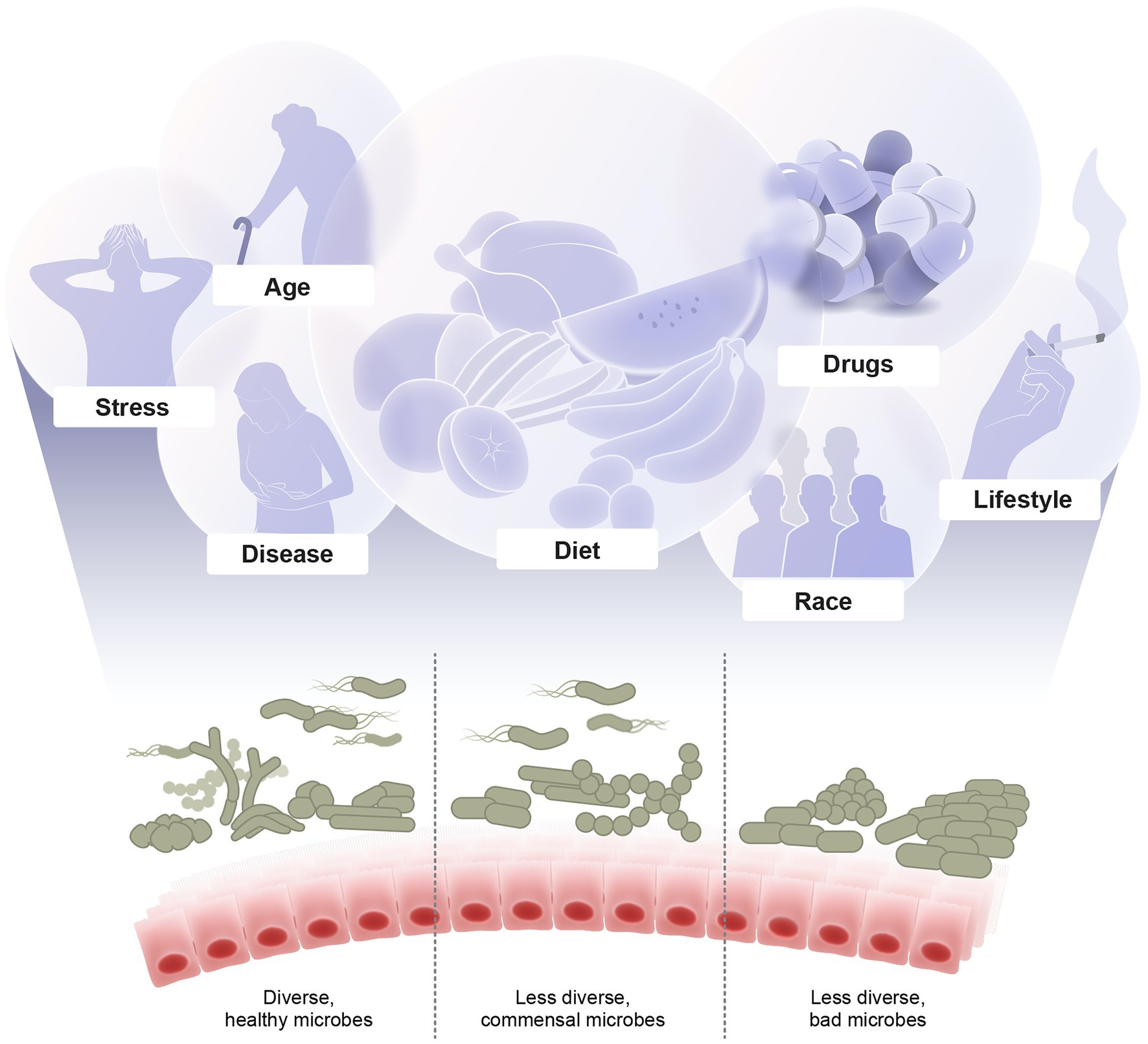
Frontiers Recent Advances In Understanding The Structure And Function Of The Human Microbiome Microbiology

Recent Advances Of Intestinal Microbiota Transmission From Mother To Infant Sciencedirect

The Role Of Microbiota In Respiratory Health And Diseases Particularly In Tuberculosis Sciencedirect

How To Get Your Microbiota To Work For You Dragonfire Nutrition In 2020 Health Nutrition Health Tips

Recent Advances Of Intestinal Microbiota Transmission From Mother To Infant Sciencedirect
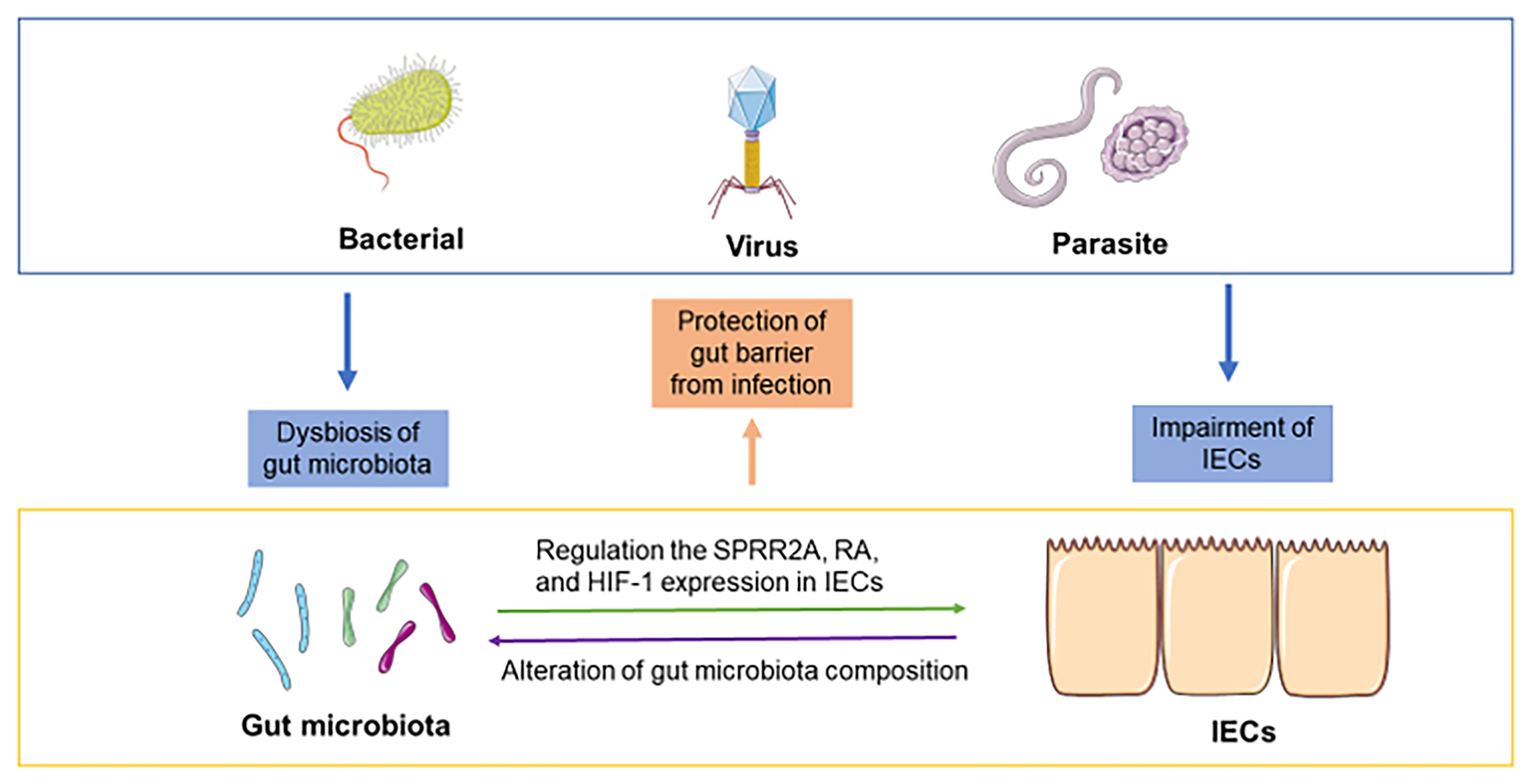
Frontiers Crosstalk Between The Gut Microbiota And Epithelial Cells Under Physiological And Infectious Conditions Cellular And Infection Microbiology

Varun Paherwar On Twitter Natural Colon Cleanse Colon Cleanse Gut Bacteria
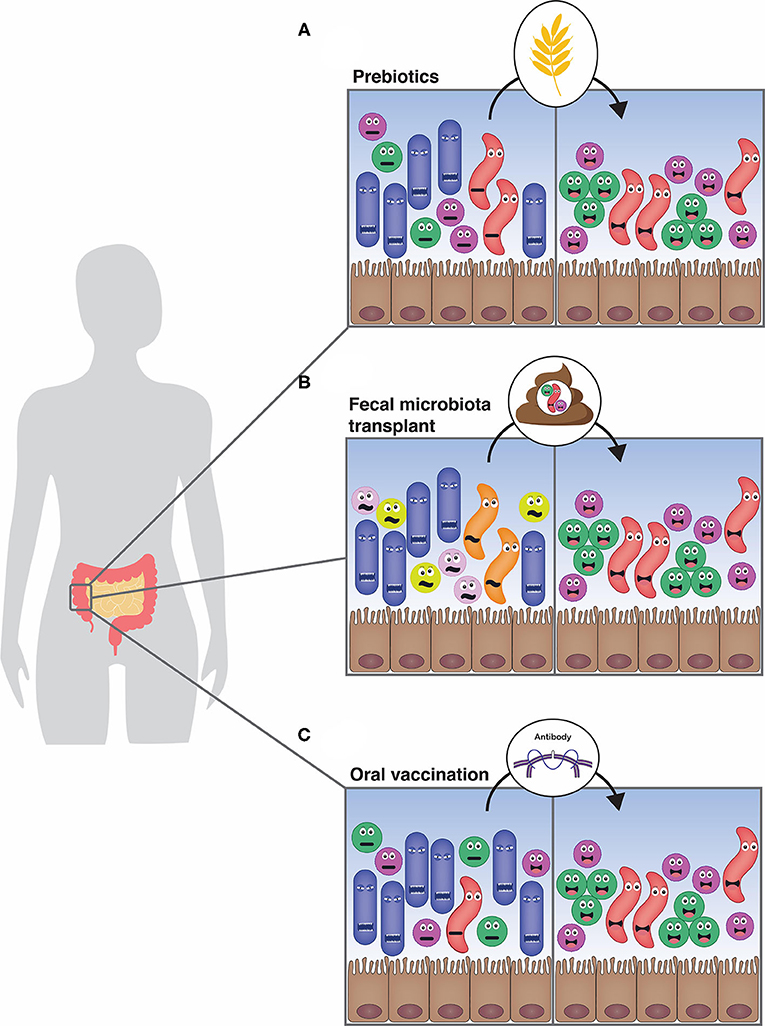
How The Gut Microbiota Influences Our Health And How We Can Influence It Frontiers For Young Minds
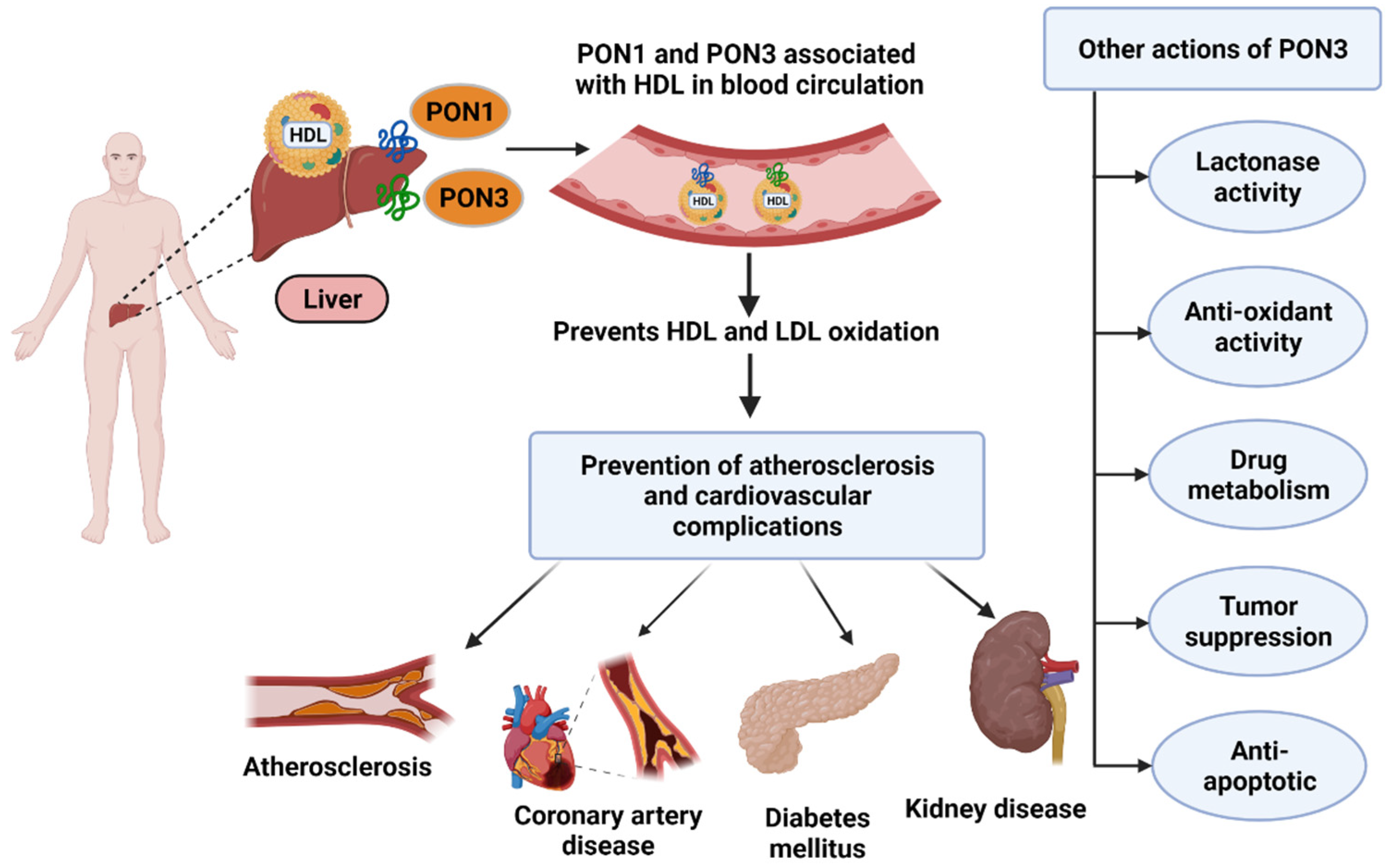
Antioxidants Free Full Text A Pon For All Seasons Comparing Paraoxonase Enzyme Substrates Activity And Action Including The Role Of Pon3 In Health And Disease Html
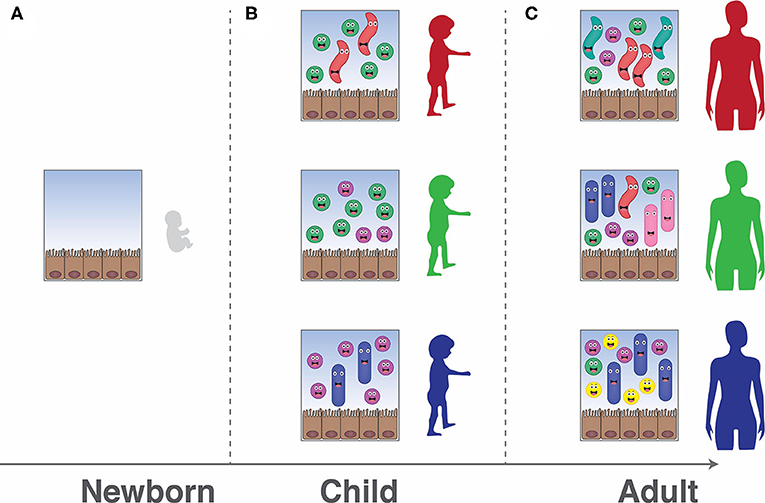
How The Gut Microbiota Influences Our Health And How We Can Influence It Frontiers For Young Minds

Pin By أبو خلاد On جهاز الهضمي Clothes Hanger Hanger

Basic Bacterial Cell Structure Bacterial Cell Structure Cell Wall Microbiology

The Role Of Microbiota In Respiratory Health And Diseases Particularly In Tuberculosis Sciencedirect

Maternal Vertical Transmission Affecting Early Life Microbiota Development Trends In Microbiology
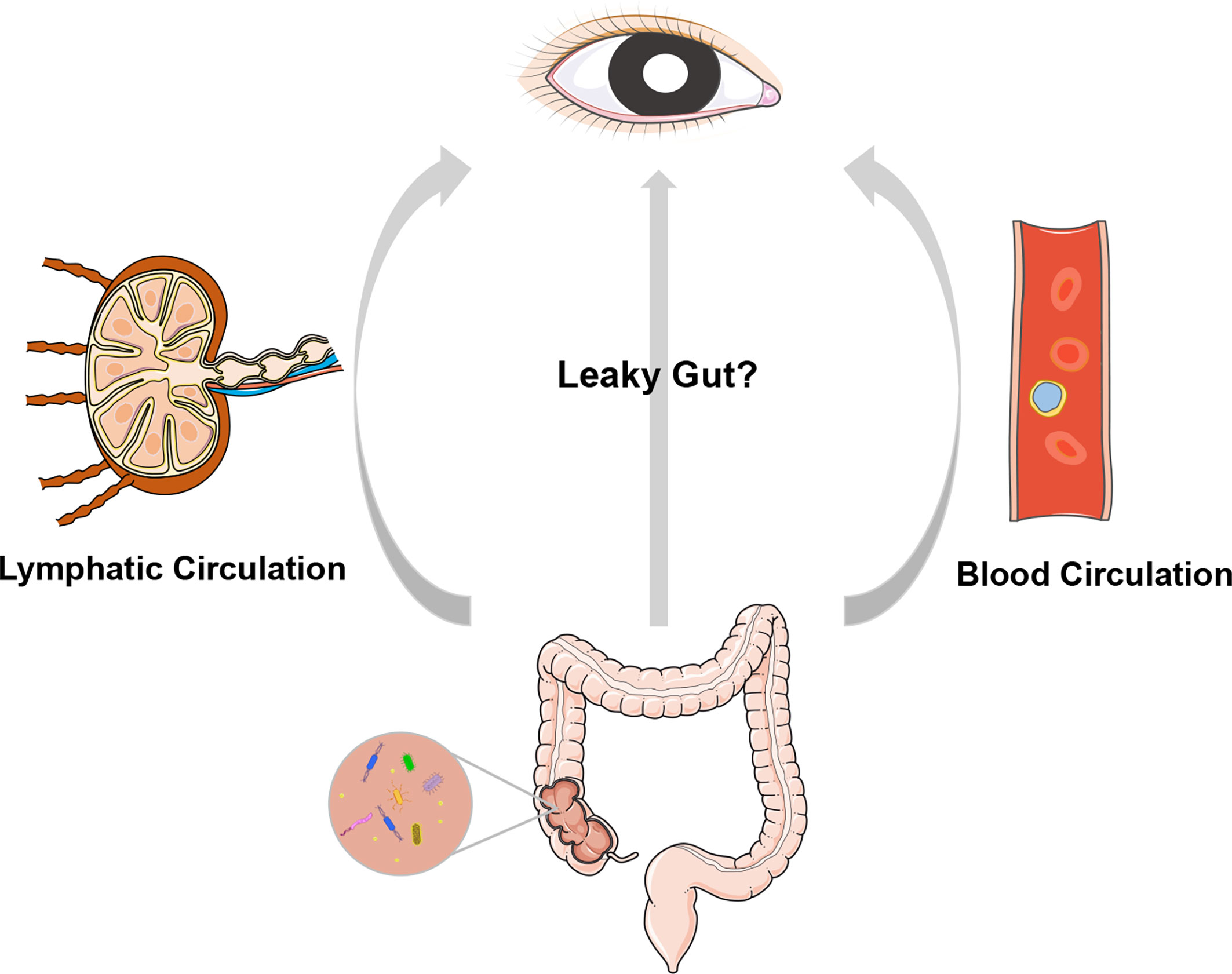
Frontiers Microbiota And Ocular Diseases Cellular And Infection Microbiology
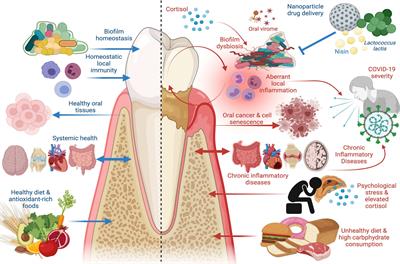
Frontiers Periodontal Disease The Good The Bad And The Unknown Cellular And Infection Microbiology
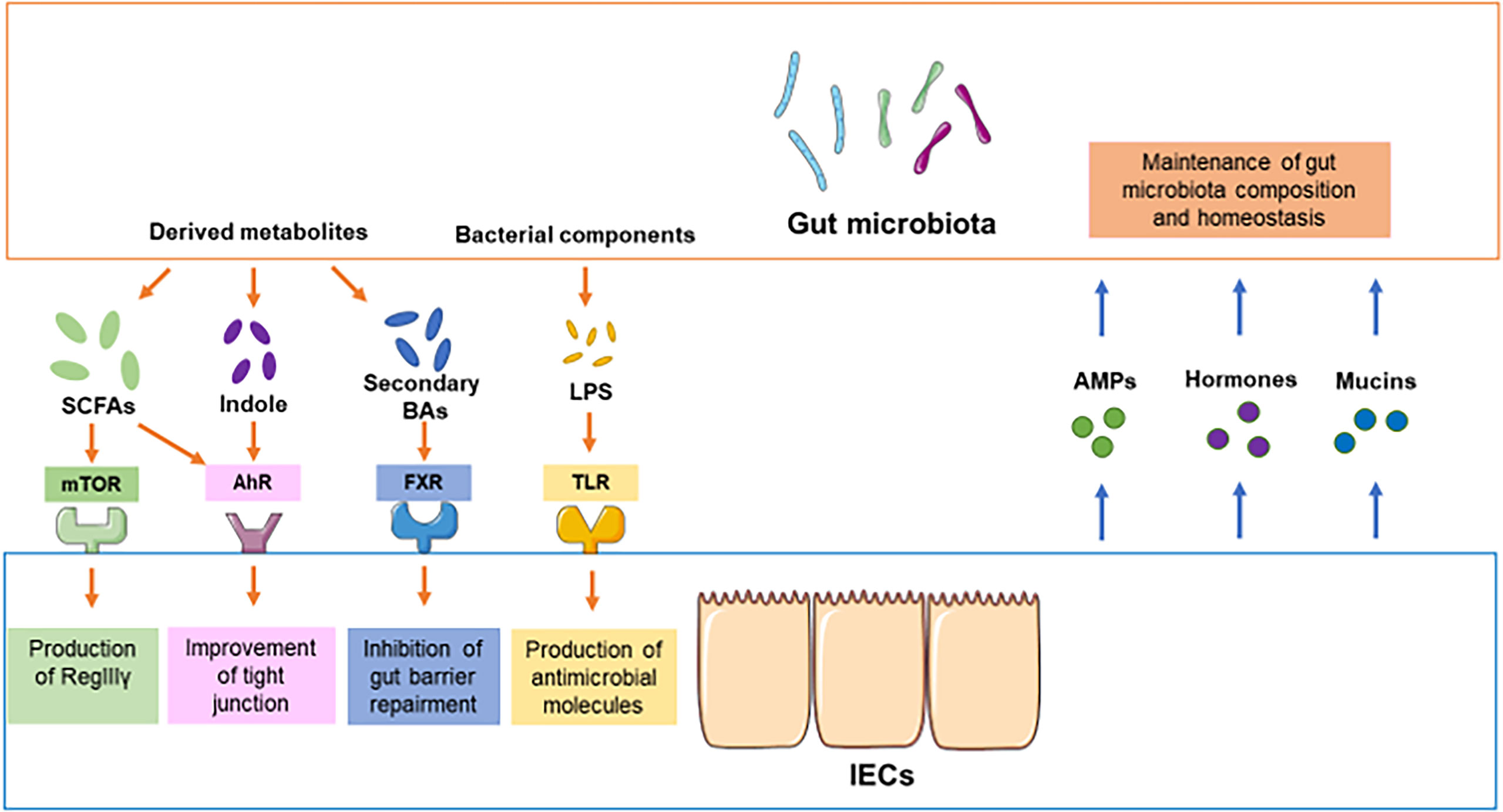
Frontiers Crosstalk Between The Gut Microbiota And Epithelial Cells Under Physiological And Infectious Conditions Cellular And Infection Microbiology


Comments
Post a Comment